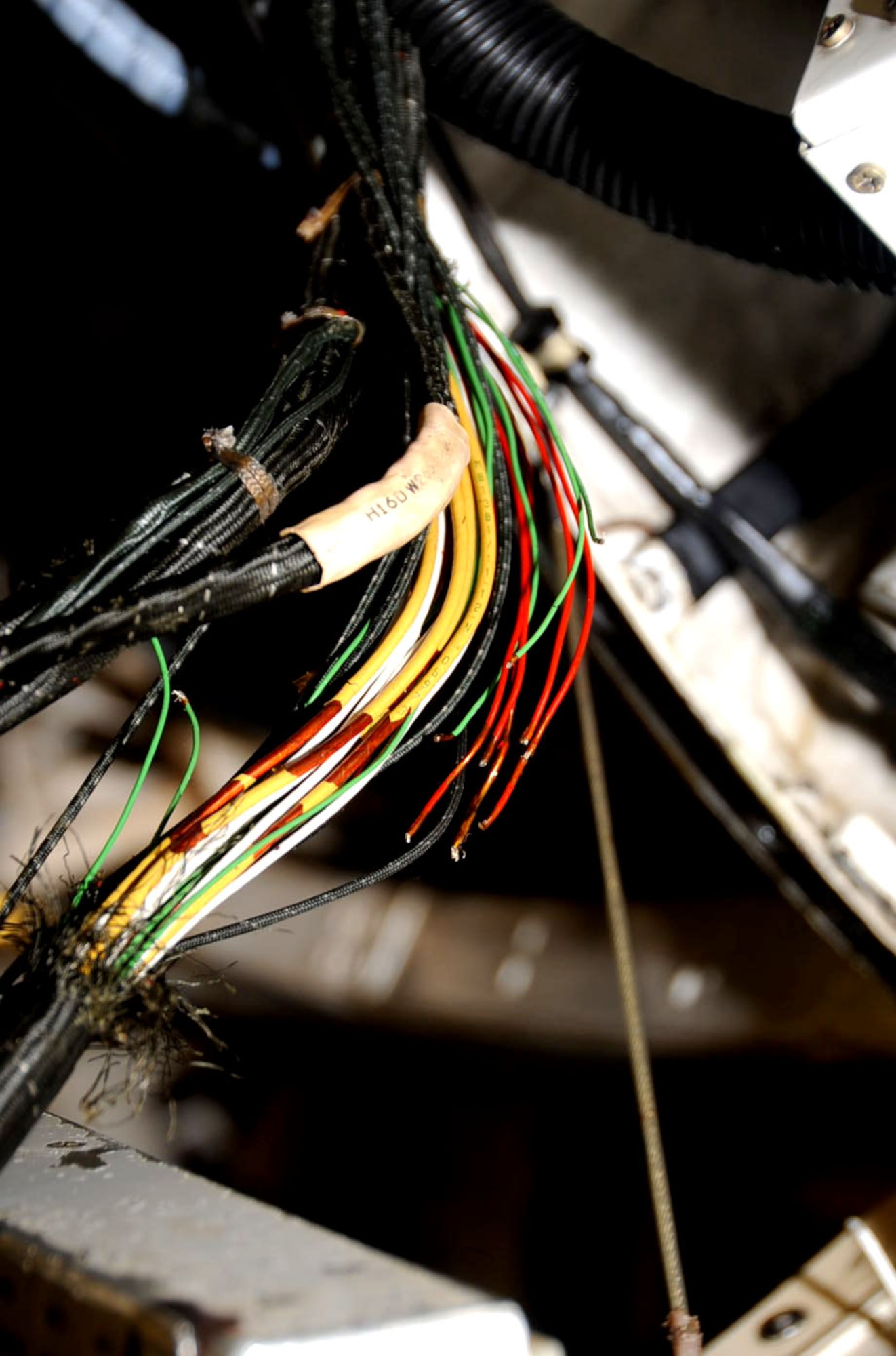
Types of Cables
페이지 정보

본문
When they stop flowing, the electricity disappears. Examples: CURRENT OF ELECTRICITY. Ampacity is determined based on the heat generated in a conductor due to the current through it. The use of such cables is highly recommended in installations where there is a risk due to the presence of various chemical agents and oils belonging to the hydrocarbon group or its derivatives. These types of electrical wires and cables are abundantly seen in installations where there is a risk of explosion and fire or in places with lots of rodents. HEPRZ1 - These medium voltage electric cables come with HEPR insulation, are halogen-free, and are not fire or flame-propagating. It offered very small outside diameter for a given current carrying capacity, good mechanical strength and of course, News excellent fire resistance. In fact, the above "cranes" do not exist, and neither does "electricity." Both are collections of completely separate concepts, but where we've given them the same name. Since copper is the best conductor, it is the body you will find in these products, which are also offered in different diameters, voltages and lengths. Copper wires in a cable may be bare, or they may be plated with a thin layer of another metal, most often tin but sometimes gold, silver or some other material.
Note that each layer has six strands more than the layer inside it. Check out the website for more information. Visit the website of the eShop, check out the products, and you can decide on the cables which would fit your requirements best. These are made from high conducting metals like Copper and Aluminum which have low resistance and can be used for high voltage applications. Flexible copper wire conductor - A flexible copper wire conductor is a set of fine wires, what are electric cables which are usually covered with an insulating material. Typically this insulating material is composed of plastic or rubber-like material. Electrical cable jacket material is usually constructed of flexible plastic which will burn. Likewise, any conductor or cable will pick up energy from any existing electromagnetic field around it. These cables are ideal for the distribution and transportation of energy in various medium-voltage networks. These effects are often undesirable, in the first case amounting to unwanted transmission of energy which may adversely affect nearby equipment or other parts of the same piece of equipment; and in the second case, unwanted pickup of noise which may mask the desired signal being carried by the cable, or, if the cable is carrying power supply or control voltages, pollute them to such an extent as to cause equipment malfunction.
The first solution to these problems is to keep cable lengths in buildings short since pick up and transmission are essentially proportional to the length of the cable. The first thermoplastic used was gutta-percha (a natural latex) which was found useful for underwater cables in the 19th century. Changes and development in lamp technology, compliance with lighting design guidance as well as styling cues can all assist in determining the age of a lighting installation however, information found relatively easily within such luminaires can often give more exact information. Cable assemblies can also take the form of a cable tree or cable harness, used to connect many terminals together. Let us take a look at different types of electrical cabling, wiring, and conductors for various electrical applications. It is used in many commercial applications and therefore is widely available and comes in a variety of different gauges. Different types of electrical wires and cables and conductors have myriad applications in communication and data transmission networks, the transmission of electric power, establishing safety connections, earthing, and so on. Usage in steady decline, but where still used - predominantly on safety circuits, red outer covering became common.
Physically, an electrical cable is an assembly consisting of one or more conductors with their own insulations and optional screens, individual coverings, assembly protection and protective covering. Shielded cable - Used for sensitive electronic circuits or to provide protection in high-voltage applications. Supporting elements - Apart from the conductor and the insulation, there are other supplementary elements in a cable which offer protection to the cable and ensure its durability and longevity. Power cables are used for bulk transmission of alternating and direct current power, especially using high-voltage cable. When the cable is buried in the ground for the transmission and distribution of electric power, it is known as an underground cable. A single-phase supply needs a line, a neutral, and a ground wire each, whereas, for a three-phase supply, three-line wires, a neutral, and a ground wire each is needed. Okhla Industrial Estate, New Delhi Ground Floor, C-47, Ground Floor Okhla, DDA Shed, Block C, New Delhi, Okhla Industrial Estate, New Delhi - 110020, Dist.

- 이전글The Complete List Of Mesothelioma Settlement Dos And Don'ts 24.09.05
- 다음글Khám Phá Hương Vị Đặc Trưng Của Rượu Tây 24.09.05
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.